fetch数据请求
在传统的请求方式里面,我们使用请求都是基于XMLHttpRequest的ajax异步请求,如果要使用这个东西,我们要手动的创建对象,并要注意兼容(因为不同浏览器创建方式是不一样的),并且操作起来还比较麻烦(它的get与post不相同),同时返回值单一
XMHttpRequest已经出来十几年了,它的技术也已经发展到瓶颈了,为了适应更复杂的数据请求(如文件下载,视频缓冲,流的处理等),现在的浏览器厂商在window对象下面新推出一个方法叫fetch请求这就造成了网络上面有一个调侃的话“传统的ajax已死,fetch永生”
核心点: fetch是基于Promise存在的,所以它返回的是一个Promise,并且是以stream流为传输对象
基础的fetch请求
fetch(url).then(resp => {
//resp代表的就是服务器返回浏览器的东西
console.log(resp);
})
这个时候得到的resp对象如下图

body代表响应的主体内容,它是一个数据流streambodyUsed当前主体内容是否已经被使用过headers服务器响应的头部信息ok代表是否请求成功redirected当前请求是否被转发过status代表响应的状态码statusText响应状态的文字type请求的类型,其中cors代表跨域。[cors:cross origin resource share跨域资源共享]url代表本次请求的url地址
刚刚我们已提过了,fetch是以流为传输对象,所以我们返回的 resp.body这是一个ReadableStream,但是我们最终想要的不一定是stream流,而一个实实在在的数据或文件,如json字符串、普通的text文件,或下载的文件。这怎么办呢
fetch在响应的对象resp里面为我们不仅仅提供了上面的属性,还为我们提供了很多的方法
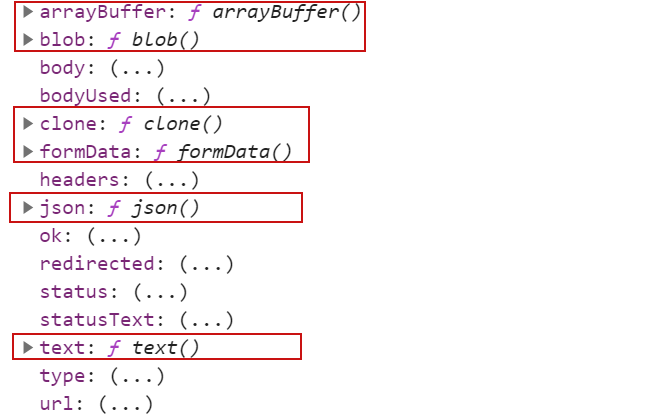
arrayBuffer将返回的数据流转换成ArrayBuffer类型blob将返回的数据流转换成blob类型clone将当前的数据流克隆一份json当前的返回的数据流转换成json字符串,再通过json字符串转换成js对象text当前的返回的数据流转换成普通的文件
上面的5个方法也同样的是异步的,也都是基于Promise存在的
例如我们要将上面请求的数据转换成json应该怎么办呢?
fetch(url).then(resp => {
//resp代表的就是服务器返回浏览器的东西
return resp.json();
}).then(json => {
console.log(json);
})
上面就是调用了一个接口,返回流以后再转换成json来进行接收
案例:使用fetch去下载一个音乐文件
let url = "http://www.softeem.xin:8888/public/musicData/24/24.mp3";
//上面的地址我们可以使用传统的ajax去请求,还可以使用fetch请求
//上面的东西返回的是一个音乐,你怎么将这个音乐文件下载下来
fetch(url).then(resp=>{
return resp.blob();
}).then(blob=>{
let tempURL = URL.createObjectURL(blob);
let a = document.createElement("a");
a.href = tempURL;
a.download="音乐文件";
a.click();
})
fetch的post请求及配置
fetch的默认情求方式是get,但是我们可以通过配置来实现post请求,并且携带参数都可以
function postRequest() {
let url = "http://www.softeem.xin/resiDentApi/Admin/checkLogin";
//一般的参数有两种
//application/x-www-form-urlencoded
//application/json
fetch(url, {
method: "POST",
headers:{
"Content-Type":"application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=UTF-8"
},
body: "adminname=yangbiao&adminpwd=123456"
}).then(resp => {
return resp.json();
}).then(json=>{
console.log(json);
})
}
post请求的参数携带是在body里面post请求一定要设置请求头的Content-Type
上面的代码中,我们的Content-Type指定的是application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=UTF-8,同时也可以定指定application/json这种格式
function postRequest() {
let url = "http://www.softeem.xin/resiDentApi/Admin/checkLogin";
//一般的参数有两种
//application/x-www-form-urlencoded
//application/json
fetch(url, {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json;charset=UTF-8"
},
body: JSON.stringify({
adminname: "yangbiao",
adminpwd: "123456"
})
}).then(resp => {
return resp.json();
}).then(json => {
console.log(json);
})
}
fetch的封装使用
const request = {
baseURL: "http://www.softeem.xin:8888",
headers: {
},
get(url) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fetch(`${this.baseURL + url}`, {
headers: {
...this.headers
}
}).then(resp => {
if (resp.status === 200) {
//请求成功
resolve(resp.json());
}
else {
reject("请求失败");
}
})
})
},
post(url, params) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fetch(`${this.baseURL + url}`, {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": typeof params === "string" ? "application/x-www-form-urlencoded" : "application/json"
, ...this.headers
},
body: typeof params === "string" ? params : JSON.stringify(params)
}).then(resp => {
if (resp.status === 200) {
resolve(resp.json());
}
else {
reject("请求失败");
}
})
});
}
}


评论区